WebHelp:Converting Formats/5.0: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (7 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Main Page|Wiki Home]] > [[{{WebHelp:Links|Content}}|MediaMonkey 5 Help]] > [[{{WebHelp:Links|Editing Tracks}}|Editing Files]] > Converting Formats | |||
MediaMonkey | |||
---- | |||
{{WebHelpHeader|Converting Formats}} | |||
Conversion is useful if you have a device that only supports one format (e.g. if have a portable MP3 player you may want to convert OGG files to MP3). MediaMonkey can convert one audio format to another audio format or one video format to another video format. MediaMonkey can also convert files to the same file type, but with different encoding settings (like a 256Kbps MP3 to a 160Kbps MP3 file). MediaMonkey can't convert video files to audio files. With video files MediaMonkey can't choose which audio or subtitle tracks should be used for the converted file. | |||
Conversion can never add quality to the converted file. So converting a lossy MP3 to a lossless FLAC does not make the audio file a FLAC quality file. When converting from a lossy compression format there may be a loss in fidelity on the converted file. However converting a lossless file to another lossless file occurs without any fidelity loss (like FLAC to ALAC). To maintain the highest possible quality for your collection, do not replace the original file. | |||
== Convert Files == | |||
To convert, select the file(s) you want to convert and use '''Tools > Convert Format''' from the Main Menu. The Convert Format dialog will appear, from which you may configure:[[File:Wiki-MM5 Convert Format.jpg|1000px|center|MediaMonkey Convert Format dialog]]<br><br> | |||
#Choose whether to replace the original files or convert the files to a new destination. | |||
#'''Destination''', the folder and filename format to be used for the converted file(s) using a [[{{WebHelp:Links|Configuring Directory and File Formats}}|Mask]]. ''Note that if the [[{{WebHelp:Links|Configuring Directory and File Formats}}|Mask]] results in the same Path as the original files that the original files will be overwritten even if not set to do so.'' | |||
#'''Format''' are the settings used to convert the file(s). Select the file type you want to use as Format and use '''Settings''' to change the settings to be used for that file type while converting the file(s). See [[{{WebHelp:Links|Basic Concepts}}|Digital Ripping & Digital File Formats]]. | |||
#''Add converted files to the library'' will add the converted files to the MediaMonkey Library. ''Note that [[{{WebHelp:Links|Adding_Existing_Files_to_the_Library}}#Using_Folder_Monitoring_to_Automatically_Update_the_Library|Folder Monitoring]] will add converted files saved in any monitored location''. | |||
#''Level Track volume'' Whether the volume of the files should be [[{{WebHelp:Links|Volume_Leveling}}#Leveling_Track_Volume|leveled]] as they are converted. [[{{WebHelp:Links|Volume_Leveling}}#Leveling_Track_Volume|Volume Leveling]] is not a lossless process. | |||
Press '''OK''' to proceed with the conversion. | |||
== Auto-Conversion == | |||
MediaMonkey offers [[{{WebHelp:Links|Auto-Conversion_Configuration}}|Auto-Conversion]] when [[{{WebHelp:Links|Exporting_Tracks}}|synchronizing]] and when [[{{WebHelp:Links|Setting_UPnP_DLNA_Media_Servers}}|streaming/casting]] to other devices. [[{{WebHelp:Links|Auto-Conversion_Configuration}}|Auto-Conversion]] will not modify the original files in your MediaMonkey Library. This allows you to maintain a library of many file types on your PC while still being able to [[{{WebHelp:Links|Exporting_Tracks}}|sync]]/[[{{WebHelp:Links|Setting_UPnP_DLNA_Media_Servers}}|stream/cast]] those files in formats the device is able to play. | |||
== Related Information == | |||
* [[{{WebHelp:Links|Configuring Directory and File Formats}}|Configuring Directory and Filename Formats]] | |||
* [[{{WebHelp:Links|Basic Concepts}}|Digital Ripping & Digital File Formats]] | |||
* [[{{WebHelp:Links|MP3 Encoding Settings}}|MP3 Encoder Settings]] | |||
* [[{{WebHelp:Links|Auto-Conversion_Configuration}}|Auto-Conversion]] | |||
{{WebHelpFooter}} | |||
Latest revision as of 22:18, 14 December 2020
Wiki Home > MediaMonkey 5 Help > Editing Files > Converting Formats
Conversion is useful if you have a device that only supports one format (e.g. if have a portable MP3 player you may want to convert OGG files to MP3). MediaMonkey can convert one audio format to another audio format or one video format to another video format. MediaMonkey can also convert files to the same file type, but with different encoding settings (like a 256Kbps MP3 to a 160Kbps MP3 file). MediaMonkey can't convert video files to audio files. With video files MediaMonkey can't choose which audio or subtitle tracks should be used for the converted file.
Conversion can never add quality to the converted file. So converting a lossy MP3 to a lossless FLAC does not make the audio file a FLAC quality file. When converting from a lossy compression format there may be a loss in fidelity on the converted file. However converting a lossless file to another lossless file occurs without any fidelity loss (like FLAC to ALAC). To maintain the highest possible quality for your collection, do not replace the original file.
Convert Files
To convert, select the file(s) you want to convert and use Tools > Convert Format from the Main Menu. The Convert Format dialog will appear, from which you may configure:
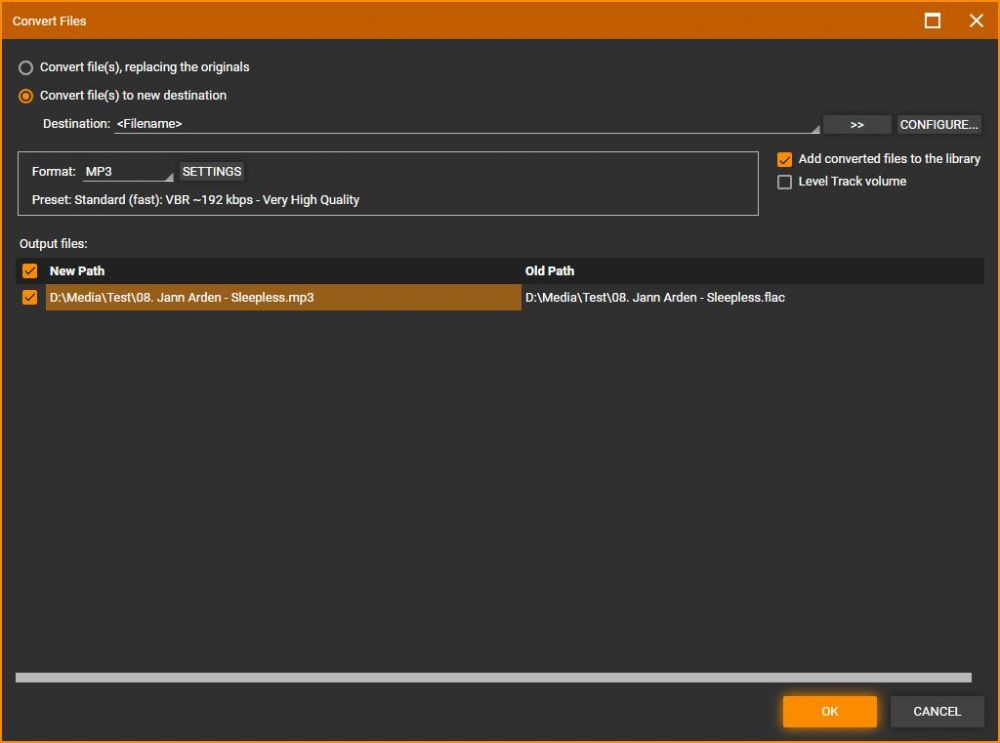
- Choose whether to replace the original files or convert the files to a new destination.
- Destination, the folder and filename format to be used for the converted file(s) using a Mask. Note that if the Mask results in the same Path as the original files that the original files will be overwritten even if not set to do so.
- Format are the settings used to convert the file(s). Select the file type you want to use as Format and use Settings to change the settings to be used for that file type while converting the file(s). See Digital Ripping & Digital File Formats.
- Add converted files to the library will add the converted files to the MediaMonkey Library. Note that Folder Monitoring will add converted files saved in any monitored location.
- Level Track volume Whether the volume of the files should be leveled as they are converted. Volume Leveling is not a lossless process.
Press OK to proceed with the conversion.
Auto-Conversion
MediaMonkey offers Auto-Conversion when synchronizing and when streaming/casting to other devices. Auto-Conversion will not modify the original files in your MediaMonkey Library. This allows you to maintain a library of many file types on your PC while still being able to sync/stream/cast those files in formats the device is able to play.
Related Information
- Configuring Directory and Filename Formats
- Digital Ripping & Digital File Formats
- MP3 Encoder Settings
- Auto-Conversion
| English |
Additional Help: Knowledge Base | Forum | MediaMonkey Support | MediaMonkey for Android Help | MediaMonkey 5 Help | MediaMonkey 4 Help